What is a Flat Foot?
In a normal foot, there is an arch which is made when the inner part of the foot is slightly raised off the ground to form an arch. This arch helps in evenly distributing the weight of the body on the feet, prevents excessive stress and helps improving balance.
People with flat foot, also known as fallen arches, have either no arch or an arch that is very low in their feet. When the arch is flattened, it allows the entire soles of the feet to touch the ground when standing. It causes over-pronation of the foot (feet may roll to the inner side when they are standing and walking) and the foot pointing outward. This causes pain in the foot and can also cause pain the calf, knee, hip or back region.
Another condition that might cause flat feet is a tarsal coalition. This condition causes the bones of the foot to fuse together unusually, resulting in stiff and flat feet.
There are several types of flatfoot, all of which have one characteristic in common: partial or total collapse (loss) of the arch. Other characteristics shared by most types of flatfoot include toe drift, in which the toes and the front part of the foot point outward. The heel tilts toward the outside and the ankle appears to turn in.
Facts about Flat Foot:
- People with flat foot tend to have an extra bone which is otherwise absent.
- The flat foot can be developed at any point in life.
- It has a long-lasting impact on legs, knees and lower back.
- Infants and toddlers have this as a very common condition.
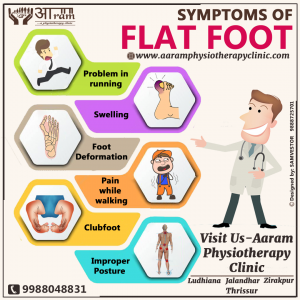
SYMPTOMS OF FLAT FOOT:
Not many people have symptoms associated with flat foot as it is not a major concern. If there is not much pain, then no treatment is usually needed.
Some symptoms of flat foot is experiencing foot pain, particularly in the heel or arch area, which might worsen with activity. Swelling might also occur with this pain in the ankle region. People with flat foot also tend to have a problem in running due to improper distribution of weight on the feet.
Flat foot also causes foot deformation while also causes pain while walking. Due to the improper distribution of body weight and hence, balance; people with flat feet tend to develop an improper posture.
HOW TO KNOW WHETHER YOU HAVE A FLAT FOOT?
If you have a lesser arch in the foot or flatness while standing, you must check whether the arches reappear or not when they placed on the bed, curled up or when tiptoed.
In some cases, the condition may worsen due to combination with other problems. The complications lead to disfiguring and distortion of the foot shape causing bunions, hammertoes and shin splints.
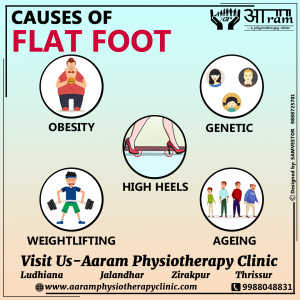
CAUSES OF FLAT FOOT:
Flat foot occurring in toddlers or infants is common as their body is still developing and arches haven’t developed much. This is a normal variation in foot type, and people without arches may or may not have problems.
Some children have flexible flatfoot, in which the arch is visible when the child is sitting or standing on tiptoes but disappears when the child stands. Arches can also fall over time. Years of wear and tear can weaken the tendon that runs along the inside of your ankle and helps support your arch.
Flat foot is also associated with other reasons being obesity, often wearing high heels, weightlifting, due to injury to ankle or foot, arthritis and some genetic reasons.
TREATMENT AND EXERCISES FOR FLAT FOOT:
Treatment for Flexible Flat Foot: Flexible Flat Foot can be corrected by strengthening of the muscles which help maintain the arch. Stretching the calf muscle (as it ensures flexibility of the foot), towel crumpling (crumple towel with toes without moving the feel), rolling the ball with your foot forward and backwards, standing on toes and walking on toes help reduce the symptoms of flat foot.
Arch supports made of silicon or embedded insoles of footwear (shoe therapy) are a good remedy to this problem and help alleviate the pain as well.
There are a lot of recommended exercises for the rehabilitation of Flat Foot.
Half Frog Pose (Ardha Bhekasana): Half Frog pose is more than a backbend; it opens the shoulders, chest, and thighs all at once.
Downward-Facing Dog (Adho Mukha Svanasana): Adho Mukha Svanasana is one of the poses in the traditional Sun Salutation sequence. It’s also an excellent yoga asana all on its own. Stay in this pose anywhere from 1 to 3 minutes. It is an extremely rejuvenating stretch.
Dolphin Pose: Opens and strengthen the shoulders, open the hamstrings, and prepare the body and mind to go upside down in Dolphin Pose.
Chair Pose (Utkatasana): Chair Pose clearly works the muscles of the arms and legs, but it also stimulates the diaphragm and heart.
Intense Side Stretch Pose (Parsvottanasana)


Comments are closed.